Stock Trading
Algorithm
June 2023
Select a version to view
Project Overview
This project implements a neural network-based stock trading system that learns optimal trading strategies through evolutionary learning. The system analyzes historical stock data (TSLA 1-minute candlesticks) and evolves a neural network to maximize a custom profit metric called the Profit Index.
Key Features:
- Custom Neural Network: Built from scratch using NumPy
- Evolutionary Learning: Weight optimization through iterative testing
- Profit Index Metric: Custom performance evaluation function
- Real-time Simulation: Backtest trading strategies on historical data
- Visualization: Learning curves and equity performance graphs
Technology Stack
Python 3.x NumPy Matplotlib
Neural Network Architecture
Network Structure
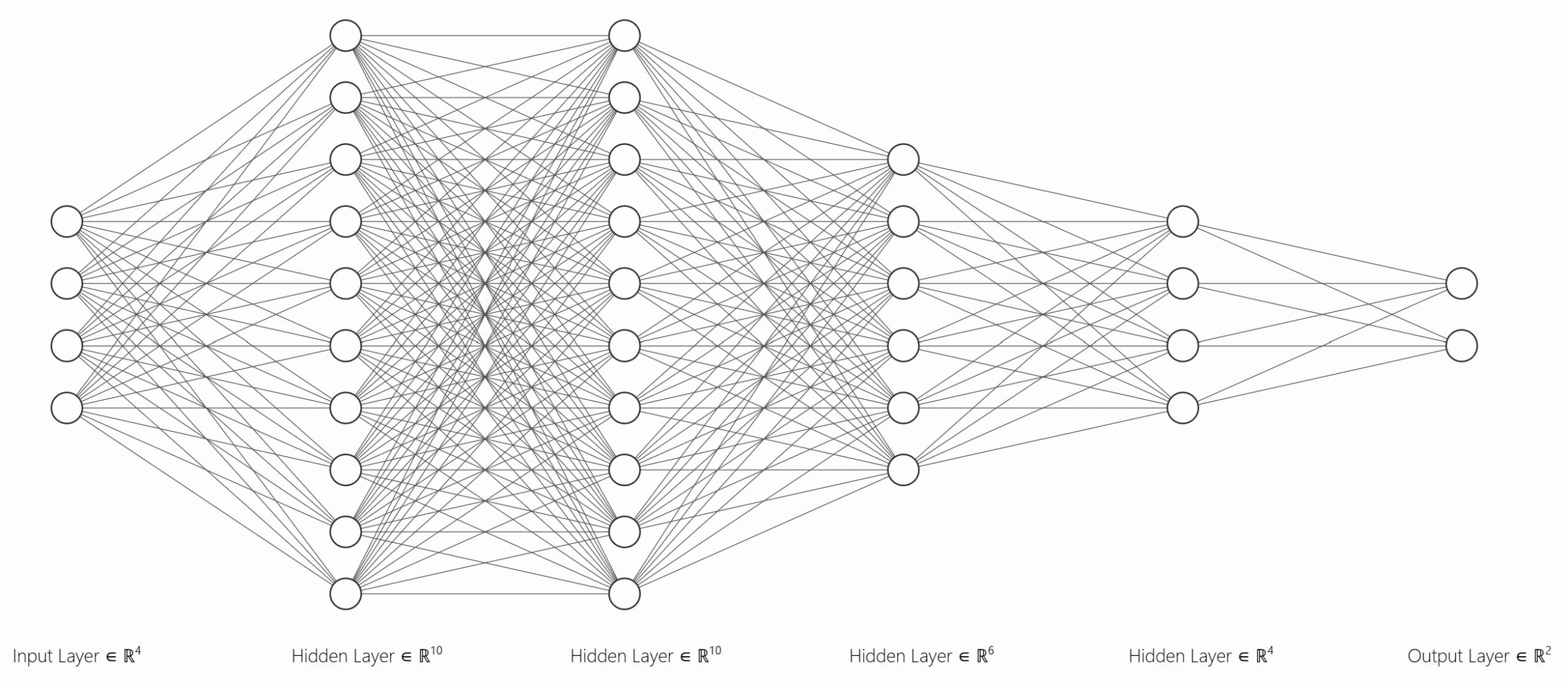
This is an exemplatory image of how a neural network looks like. Note that the layer size is depicted less complex for visualization purposes.
Layer Configuration: [40] → [100] → [100] → [60] → [20] → [2]
Input Layer → Hidden Layers (ReLU) → Output Layer (Softmax)
| Layer | Type | Neurons | Activation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Dense | 40 | - | 20 candles × 2 features (price + volume) |
| Hidden 1 | Dense | 100 | ReLU | Feature extraction |
| Hidden 2 | Dense | 100 | ReLU | Pattern recognition |
| Hidden 3 | Dense | 60 | ReLU | Feature reduction |
| Hidden 4 | Dense | 20 | ReLU | Decision preparation |
| Output | Dense | 2 | Softmax | Buy/Sell probabilities |
Input Features
The network processes 20 consecutive 1-minute candles with the following features:
- Open Price: Opening price of each candle
- Volume: Trading volume for each candle
- Moving Average: 20-period simple moving average
Output Layer
The network outputs two probability values:
- Buy Signal [0]: Confidence in upward price movement
- Sell Signal [1]: Confidence in downward price movement
Learning Algorithm
Profit Index Calculation
The system uses a custom metric called the Profit Index to evaluate neural network performance:
class ProfitIndex:
def forward(self, y_pred, price_changes):
sum = 0
for i, dataset in enumerate(y_pred):
y_pred_clipped = np.clip(dataset, 1e-7, 1-1e-7)
# Extract confidence (0 to 0.5 range)
max_confidence = np.max(y_pred_clipped, axis=1) - 0.5
# Determine direction: +1 for buy, -1 for sell
direction = (np.argmax(y_pred_clipped, axis=1) * (-2)) + 1
# Calculate weighted profit
sum += np.dot(max_confidence, direction) * price_changes[i]
return sum / n_datasets_per_genWeight Optimization Strategy
1. Initialization
self.weights = 0.1 * np.random.randn(n_inputs, n_neurons)
self.biases = np.zeros((1, n_neurons))2. Iterative Modification
The system uses two modification strategies:
def modify_weights():
for layer in layers:
layer.type.weights += variation_factor * np.random.randn(n_inputs, n_neurons)
layer.type.biases += variation_factor * np.random.randn(1, n_neurons)def modify_partial_weights():
for layer in layers:
rw = randrange(len(layer.type.weights))
rb = randrange(len(layer.type.biases))
layer.type.weights[rw-1] += variation_factor * np.random.randn(layer.type.n_neurons)
layer.type.biases[0][rb-1] += variation_factor * np.random.randn(1)3. Selection Process
for iteration in range(n_generations):
# Modify weights
if iteration % 10 == 0:
modify_partial_weights()
else:
modify_weights()
# Test new configuration
load_data()
output = process_inputs()
pi = ProfitIndex().forward(output, Y)
# Keep if better, revert if worse
if pi > best_profit_index:
saveWeightsBiases()
best_profit_index = pi
else:
loadBestWeightsBiases()Activation Functions
ReLU (Hidden Layers)
class Activation_ReLU:
def forward(self, inputs):
self.output = np.maximum(0, inputs)Custom Softmax (Output Layer)
Modified softmax with decision bias parameter:
class Activation_Softmax:
def forward(self, inputs):
# Normalize with decision bias
values = inputs / ((abs(np.max(inputs, axis=1, keepdims=True)) +
abs(np.min(inputs, axis=1, keepdims=True)) * decision_bias))
# Apply exponential normalization
self.output = np.exp(values) / (np.max(np.exp(values)) +
np.min(np.exp(values)))How This Model Learns
The learning process works through trial and error:
- Start with a random guess - The model begins with random weights (like a student guessing without knowledge)
- Make predictions - It analyzes 200 random time windows from the stock data and predicts whether prices will go up or down
- Score the performance - A "Profit Index" measures how good those predictions were (like grading a test)
- Randomly tweak the understanding - The model makes small random adjustments to its weights and biases (like the student trying a slightly different approach)
- Keep improvements, discard failures - If the new predictions score better, keep the changes. If worse, revert back to the previous version
- Repeat 300 times - This cycle runs 300 generations, gradually finding better and better configurations
- Lower bias (0.05): More extreme decisions (72% buy vs 28% sell)
- Higher bias (0.15): More balanced decisions (58% buy vs 42% sell)
Implementation Details
Configuration Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
n_neurons |
[100, 100, 60, 20] | Hidden layer neuron counts |
n_candles |
20 | Candlesticks per input window |
variation_factor |
0.001 | Weight modification magnitude |
n_datasets_per_gen |
200 | Training samples per generation |
n_generations |
300 | Total optimization iterations |
decision_bias |
0.15 | Buy/sell differentiation strength |
Data Loading Process
def load_data():
with open('TSLA_1min_sample.txt') as input_file:
X.clear()
Y.clear()
line_ranges = []
# Generate random time windows
for iteration in range(n_datasets_per_gen):
i = np.random.randint(dataset_line_number - n_candles)
line_ranges.append([i, i + n_candles - 1])
X.append([])
moving_average.append(0)
# Parse candlestick data
for i, line in enumerate(input_file):
for num_dataset in range(n_datasets_per_gen):
if i >= line_ranges[num_dataset][0] and i <= line_ranges[num_dataset][1]:
datetime_input, data_open, high, low, close, volume = (
item.strip() for item in line.split(',', 5))
X[num_dataset].append(float(data_open))
X[num_dataset].append(float(volume))
moving_average[num_dataset] += float(data_open)
if i == line_ranges[num_dataset][1]:
# Calculate target (price change percentage)
Y.append(((float(close) - float(data_open)) /
float(data_open)) * 100)
# Add moving average feature
moving_average[num_dataset] *= (1 / n_candles)
X[num_dataset].append(moving_average[num_dataset])Forward Propagation
def process_inputs():
outputs = []
for dataset in X:
# First layer
layers[0].type.forward(dataset)
layers[0].function.forward(layers[0].type.output)
# Remaining layers
for i, layer in enumerate(layers[1:]):
layer.forwardType(layers[i].function.output)
layer.forwardFunction(layer.type.output)
outputs.append(layers[-1].function.output)
return outputsTrading Simulation
After training, the system runs a realistic trading simulation to evaluate actual performance.
Simulation Parameters
- Starting Capital: $1,000
- Position Sizing: Dynamic based on signal confidence
- Test Period: ~8,248 minutes of historical data
- Asset: Tesla (TSLA) stock
Position Management
The system dynamically adjusts position sizes based on prediction confidence:
def execute_trade(response, currentPrice, equity):
if response[0][0] > response[0][1]: # Buy signal
confidence = response[0][0]
position_size = (confidence - 0.5) * 2 * equity
shares = position_size / currentPrice
print(f"Buy {shares:.2f} shares worth ${position_size:.2f}")
else: # Sell signal
confidence = response[0][1]
position_size = -(confidence - 0.5) * 2 * equity
shares = position_size / currentPrice
print(f"Sell {-shares:.2f} shares worth ${abs(position_size):.2f}")Performance Metrics
The simulation tracks multiple performance indicators:
- Total Equity: Cash + Position Value
- Percentage Return: (Final Equity / Initial Capital) - 1
- Outperformance: Strategy Return / Buy-and-Hold Return
- Profit Index: Risk-adjusted performance metric
Training Process
During training, you'll see output like:
---------------START DEEP LEARNING----------------
LAYER FIRST
LAYER NR 0
LAYER NR 1
LAYER NR 2
LAYER NR LAST
Iteration 0 done, ProfitIndex: 0.0123
Better Configuration found in Iteration 15, ProfitIndex: 0.0187
Better Configuration found in Iteration 42, ProfitIndex: 0.0234
Iterations 10% completed
Better Configuration found in Iteration 89, ProfitIndex: 0.0301
Iterations 20% completed
...
Iterations 100% completed
All iterations done! Time passed: 245 secondsSimulation Output
---------------START TRADING SIMULATION----------------
Line ranges: [1523, 9771]
Bought 45.32 Shares worth $982.50
Sold 12.15 Shares worth $265.80. Profit: $18.45
...
ENDING EQUITY: 1156.78
ENDING OUTPERFORM: 1.23- Final equity of $1,156.78 represents a 15.68% return
- Outperformance of 1.23 means the strategy beat buy-and-hold by 23%
- This signals strong model performance at first glance
Performance Analysis
Visualization
To analyze, whether the results were truly as promising as they seemed the following comprehensive performance visualizations were generated:
Trading Performance Graph
- Blue Line: Strategy equity percentage change
- Red Line: Stock price percentage change
- Green Line: Outperformance ratio
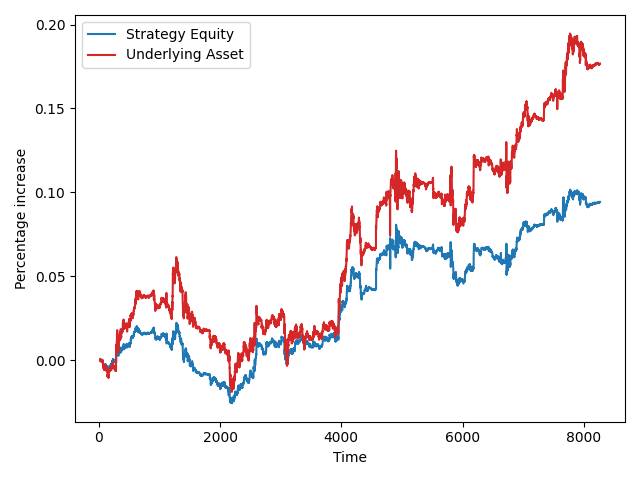
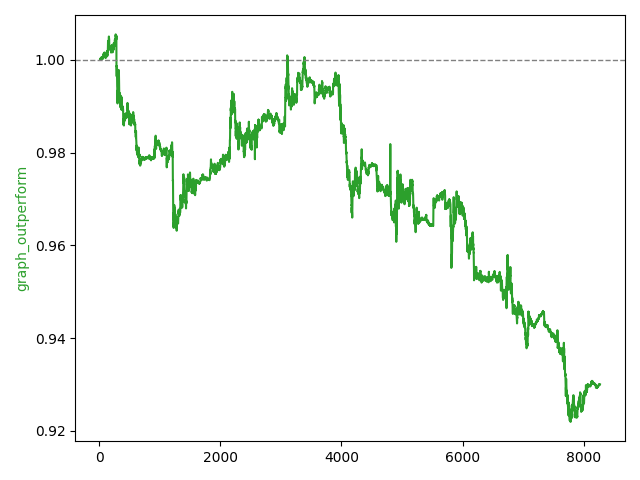
Immediately, it is obvious that instead of scalping the markets, the bots success was due to the great performance of the underlying asset. In long term, the strategy severely underperforms the buy-and-hold strategy even when simulated multiple times.
Learning Curve Graph
- Green Line: Best Profit Index over generations
- Red Line: Test Profit Index per iteration
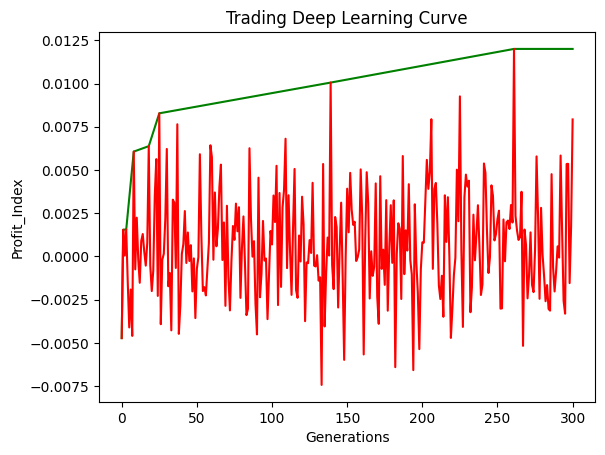
This hypothesis is further supported by the learning curve graph, which shows that the model does not seem to learn meaningful relationships. Instead, it randomly finds profitable strategies that most likely resemble unprecise forms of the "buy-and-hold" strategy. Due to fluctuations in confidence, the model randomly fails to hold or even sells the asset and misses out on equity gains, underperforming "buy-and-hold".
Due to limited available free market data the outcome of this project was never to create a perfectly working model. This is why i stopped development at this point, as in my opinion the model coming up with a profitable strategy (even if it is a worse verison of buy-and-hold) is a (small) success. Preventing the model from falling into this 'local minimum' would take lots of time and ML experience which I did not have at that point in time.
Learnings
Key Takeaways:
- Due to significant underperformance and clear learning issues, the model is not viable for practical use
- However, this project provided me with valueable, deep insights and enhanced my understanding of machine learning and the technical foundations behind popular libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Since the completion of this project, more than 2 years have passed. In the meantime, my knowledge and skills in machine learning have significantly advanced. If i were to continue this project today there is a lot of things, i would do differently. Some of them iclude:
Opportunities for future enhancement
- Switching to a library like TensorFlow would simplify model development and give opportunity to focus on improving model significance and performance
- More technical input features like indicators (RSI, MACD, price momentum) could be incorporated
- Proper training and validation splits to avoid overfitting and data leakage
- Use a recurrent network (instead of Dense Layers) to capture temporal dependencies in the time-series stock price data
- Use gradient-based optimization for more efficient training
- Normalize input features (volume has a different scale than stock price)
- Detrend the market data or use more data from more diverse market conditions
Neural Network Stock Trading System
A learning-focused machine learning project built entirely from scratch — demonstrating my ability to design, optimize, and evaluate neural networks without relying on pre-built ML frameworks.
Project Overview
This project is a self-built neural network trading system that analyzes minute‑level stock data and attempts to generate buy/sell decisions. The focus of this project was not to build a profitable trading bot, but to fully understand how neural networks work at the lowest level — from matrix operations to training logic.
Why this project matters:
- I implemented a complete neural network using only NumPy — no TensorFlow, PyTorch, or ML libraries.
- I created a custom learning and evaluation strategy to optimize the model.
- I simulated trading decisions and evaluated them with a performance metric I designed myself.
- The project shows my ability to work independently, build complex systems, and quickly learn advanced ML concepts.
How the System Works
The model takes short windows of historical TSLA price data and outputs a probability for buying or selling. Instead of classical backpropagation, I used a simple evolutionary strategy, repeatedly adjusting the model’s weights and keeping the best-performing version.
Key Components
- Custom Neural Network: Several fully connected layers coded manually.
- Evolutionary Training: Small informed changes to the model, keeping better-performing generations.
- Profit Index: My own scoring function to judge trading performance.
Simulation & Testing
I ran the model across historical 1‑minute TSLA data, simulating buy/sell decisions. The Profit Index rewarded:
- Correct direction predictions
- High-confidence decisions
- Stable, repeatable performance over many data slices
Results
While the system did not produce a profitable trading strategy, it successfully demonstrated that:
- I can independently design and implement a multi-layer neural network.
- I understand how data preprocessing, weight initialization, activation functions, and output interpretation work under the hood.
- I can build custom evaluation metrics and training loops without relying on existing tools.
What I Learned
This project provided deep, practical intuition about modern machine learning. Key learnings include:
- How neural networks behave internally (beyond high-level libraries)
- How to structurally debug ML models and interpret unstable learning behavior
- The challenges of financial time‑series prediction
- How to design experiments, evaluate performance, and iterate methodically
Neural Network Stock Trading System
A learning-focused machine learning project built entirely from scratch — demonstrating my ability to design, optimize, and evaluate neural networks without relying on pre-built ML frameworks.
Project Overview
This project is a self-built neural network trading system that analyzes minute‑level stock data and attempts to generate buy/sell decisions. The focus of this project was not to build a profitable trading bot, but to fully understand how neural networks work at the lowest level — from matrix operations to training logic.
Why this project matters:
- I implemented a complete neural network using only NumPy — no TensorFlow, PyTorch, or ML libraries.
- I created a custom learning and evaluation strategy to optimize the model.
- I simulated trading decisions and evaluated them with a performance metric I designed myself.
- The project shows my ability to work independently, build complex systems, and quickly learn advanced ML concepts.
How the System Works
The model takes short windows of historical TSLA price data and outputs a probability for buying or selling. Instead of classical backpropagation, I used a simple evolutionary strategy, repeatedly adjusting the model’s weights and keeping the best-performing version.
Key Components
- Custom Neural Network: Several fully connected layers coded manually.
- Evolutionary Training: Small informed changes to the model, keeping better-performing generations.
- Profit Index: My own scoring function to judge trading performance.
Architecture

Illustration of the multi-layer network used (simplified for visualization).
Simulation & Testing
I ran the model across historical 1‑minute TSLA data, simulating buy/sell decisions. The Profit Index rewarded:
- Correct direction predictions
- High-confidence decisions
- Stable, repeatable performance over many data slices
Results
While the system did not produce a profitable trading strategy, it successfully demonstrated that:
- I can independently design and implement a multi-layer neural network.
- I understand how data preprocessing, weight initialization, activation functions, and output interpretation work under the hood.
- I can build custom evaluation metrics and training loops without relying on existing tools.
What I Learned
This project provided deep, practical intuition about modern machine learning. Key learnings include:
- How neural networks behave internally (beyond high-level libraries)
- How to structurally debug ML models and interpret unstable learning behavior
- The challenges of financial time‑series prediction
- How to design experiments, evaluate performance, and iterate methodically
Overview
This project explores how machine learning (ML) can be used to predict short-term stock price movements.
Inspired by a YouTube video on algorithmic trading, I decided to rebuild and improve a similar model from scratch in Python to better understand the fundamentals of Neural Networks.
The goal was not to create a profitable trading algorithm, but to learn the underlying mechanics of predictive financial modeling and backtesting.